Research & Facilities
The MQO group investigates fundamental physics and develops quantum applications with mesoscopic-sized quantum states of light, all underpinned by enabling technology. Mesoscopic quantum optical states comprise 10s, 100s and 1000s of nonclassically-distributed photons. From a fundamental perspective, they can be used to explore quantum physics at energy scales that are visible to the human eye. In addition, this scale is crucial for demonstrating a genuine quantum enhancement over classical schemes in many areas including metrology, computation and communication.
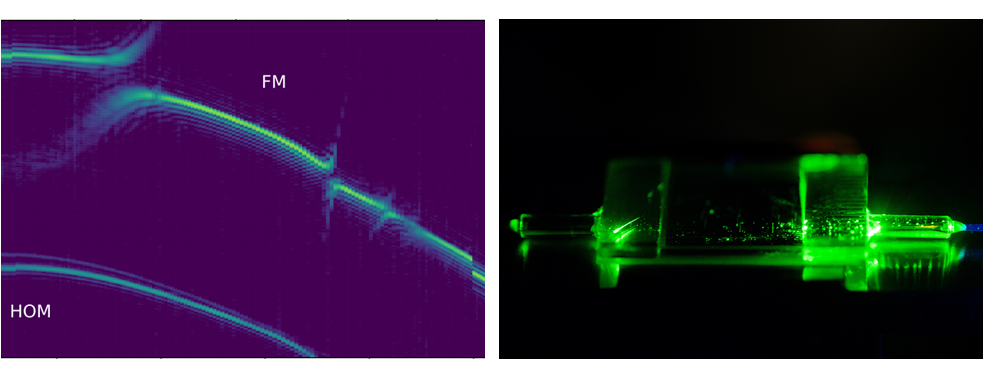
To study these systems, we use integrated optical circuits based on titanium in-diffused waguides in lithium niobate, in combination with superconducting detectors. This means that much of the nonlinear optical properties of lithium niobate must be re-optimised to function in a low-temperature environment.
In this context, the research of the MQO group can be divided into three interrelated areas: detector architectures for mesoscopic quantum optics, fundamentals of low-temperature nonlinear optics and device development for low-temperature integrated optical quantum technologies.
Our research fields
As the number of photons in quantum optical systems increases, suitable detectors need to be built and characterised to measure these systems. We develop integrated detector solutions based on in-line arrays of superconducting detectors, as well as other detector multiplexing strategies, to measure bright photonic states. Furthermore, we develop tools to characterise the outputs of such detectors in a way that reveals the quantum optical characteristics of the detected light.
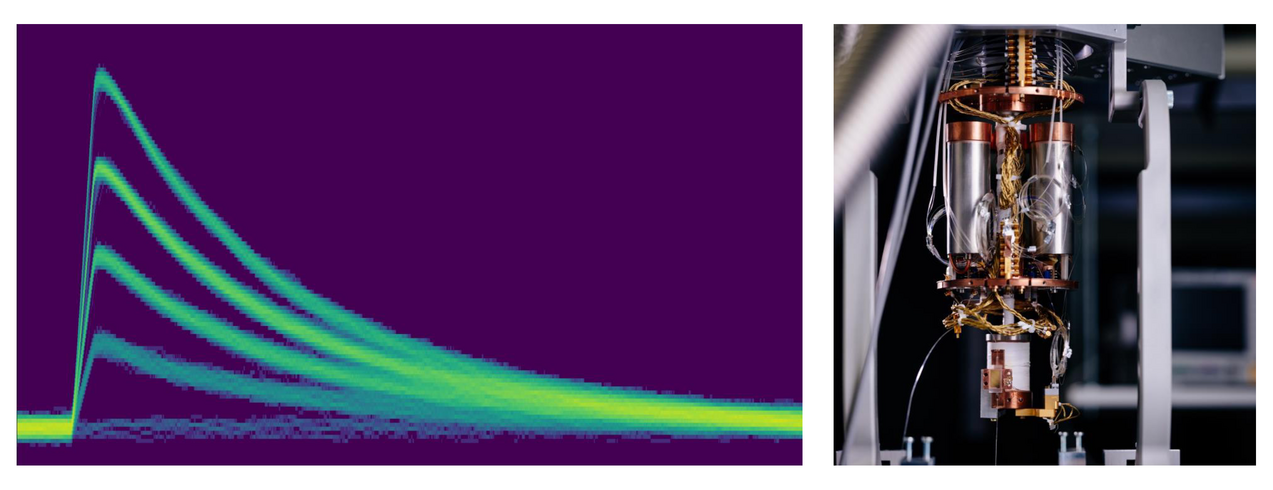
When combining integrated nonlinear optics with superconducting components, these devices must be run at very low temperatures. We investigate how the nonlinear optical properties of lithium niobate behave at a temperature approaching absolute zero, and develop functional components that function reliably under these challenging operating conditions. This includes the necessary packaging of such devices, which is the efficiect, low-temperature compatible interfacing of the integrated device and optical fibre.