Manipulation of Quantumemitters
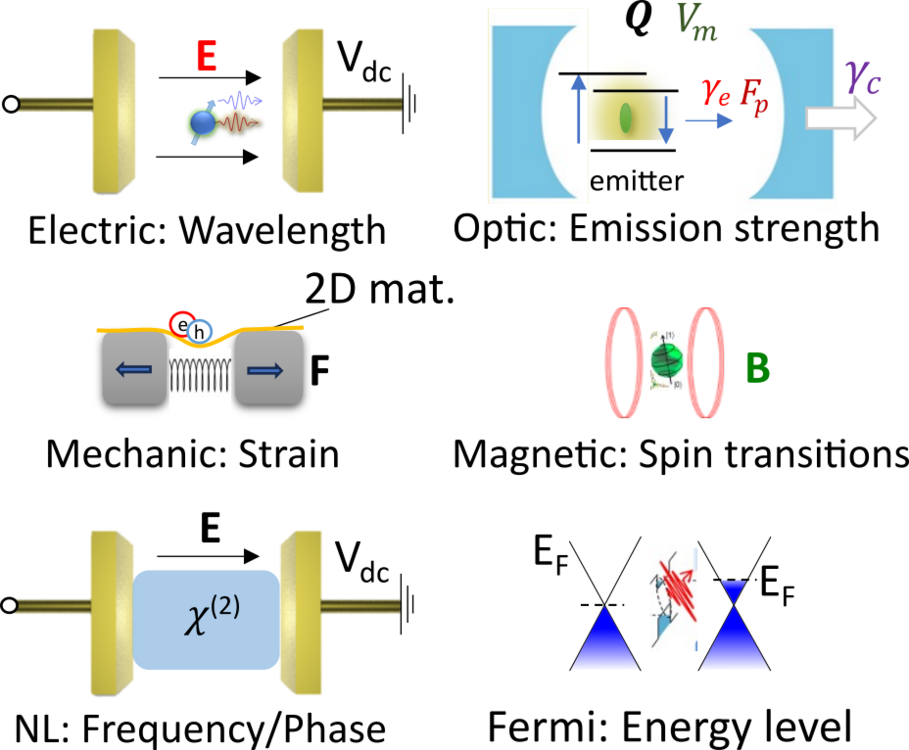
The properties of a quantum emitter are not inherently fixed but can be externally manipulated through several fundamental effects. Our research group is dedicated to exploring and implementing these "active quantum interfaces."
We also investigate materials with promising properties for single-photon sources and nodes for photon-spin interaction. Rare earth elements, such as erbium, play a particularly important role in this context. Erbium emits at the crucial telecommunication wavelength of around 1550 nm, enabling signal transmission over long distances via optical fibers.
Additionally, we are highly interested in coupling photons to already developed qubit platforms. The design of the respective optical interface is particularly critical for this purpose. The manipulation of the electronic and optical properties of emitters and quantum interfaces is carried out in 1D systems, such as waveguides, as well as in 2D systems, such as metamaterials.
Güsken, N.A., Fu, M., Zapf, M. et al. Emission enhancement of erbium in a reverse nanofocusing waveguide. Nat Commun 14, 2719 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38262-6
Ourari, S., Dusanowski, Ł., Horvath, S.P. et al. Indistinguishable telecom band photons from a single Er ion in the solid state. Nature 620, 977–981 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06281-4
Yong Yu et al., Frequency Tunable, Cavity-Enhanced Single Erbium Quantum Emitter in the Telecom Band, PRL 131, 170801 (2023), https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.131.170801
Solntsev, A.S., Agarwal, G.S. & Kivshar, Y.S. Metasurfaces for quantum photonics. Nat. Photonics 15, 327–336 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00793-z
